Introduction
Background
Bantu-speaking people settled in the area now called Angola in 6th century A.D.; by the 10th century various Bantu groups had established kingdoms, of which Kongo became the most powerful. From the late-14th to the mid-19th century, a Kingdom of Kongo stretched across central Africa from present-day northern Angola into the current Congo republics. It traded heavily with the Portuguese who, beginning in the 16th century, established coastal colonies and trading posts and introduced Christianity. Angola became a major hub of the transatlantic slave trade conducted by the Portuguese and other European powers -- often in collaboration with local kingdoms, including the Kongo. The Angola area is estimated to have lost as many as 4 million people as a result of the slave trade. The Kingdom of Kongo’s main rival was the Kingdom of Ndongo to its south, whose most famous leader was Nzingha Mbande, the 17th century diplomat to the Portuguese and later Queen, who successfully fought off Portuguese encroachment during her nearly 40-year reign. Smaller kingdoms, such as the Matamba and Ngoyo, often came under the control of the Kongo or Ndongo Kingdoms. During the Berlin Conference of 1884-85, Portugal and other European powers set Angola’s modern borders, but the Portuguese did not fully control large portions of the territory. Portugal gained control of the Kingdom of Kongo in 1888 when Kongo’s King Pedro V sought Portuguese military assistance in exchange for becoming a vassal. After a revolt in 1914, Portugal imposed direct rule over the colony and abolished the Kongo Kingdom.
The Angolan National Revolution began in 1961, and in 1975, Angola won its independence when Portugal’s dictatorship fell, a collapse that occurred in part because of growing discontent over conflict in Angola and other colonies. Angola’s multiple independence movements soon clashed, with the Popular Movement for Liberation of Angola (MPLA), led by Agostinho NETO, taking power and the National Union for the Total Independence of Angola (UNITA), led by Jonas SAVIMBI, emerging as its main competitor. After NETO’s death in 1979, Jose Eduardo DOS SANTOS, also of the MPLA, became president. Over time, the Angolan civil war escalated and became a major Cold War conflict, with the Soviet Union and Cuba supporting the MPLA and the US and South Africa supporting UNITA. Up to 1.5 million lives may have been lost -- and 4 million people displaced -- during the more than a quarter-century of fighting. SAVIMBI's death in 2002 ended UNITA's insurgency and cemented the MPLA's hold on power. DOS SANTOS did not seek reelection in 2017 and supported Joao LOURENCO’s successful bid to become president. LOURENCO was reelected in 2022. Angola scores low on human development indexes despite using its large oil reserves to rebuild since 2002.
Visit the Definitions and Notes page to view a description of each topic.
Geography
Location
Southern Africa, bordering the South Atlantic Ocean, between Namibia and Democratic Republic of the Congo
Geographic coordinates
12 30 S, 18 30 E
Map references
Africa
Area - comparative
about eight times the size of Georgia; slightly less than twice the size of Texas
Land boundaries
total: 5,369 km
border countries (4): Democratic Republic of the Congo 2,646 km (of which 225 km is the boundary of discontiguous Cabinda Province); Republic of the Congo 231 km; Namibia 1,427 km; Zambia 1,065 km
Coastline
1,600 km
Maritime claims
territorial sea: 12 nm
contiguous zone: 24 nm
exclusive economic zone: 200 nm
Climate
semiarid in south and along coast to Luanda; north has cool, dry season (May to October) and hot, rainy season (November to April)
Terrain
narrow coastal plain rises abruptly to vast interior plateau
Elevation
highest point: Moca 2,620 m
lowest point: Atlantic Ocean 0 m
mean elevation: 1,112 m
Natural resources
petroleum, diamonds, iron ore, phosphates, copper, feldspar, gold, bauxite, uranium
Land use
agricultural land: 36.8% (2022 est.)
arable land: 4.3% (2022 est.)
permanent crops: 0.3% (2022 est.)
permanent pasture: 32.3% (2022 est.)
forest: 52.5% (2022 est.)
other: 10.6% (2022 est.)
Irrigated land
860 sq km (2014)
Major rivers (by length in km)
Rio Zambeze (Zambezi) (shared with Zambia [s], Namibia, Botswana, Zimbabwe, and Mozambique [m]) - 2,740 km; Rio Cubango (Okavango) river source (shared with Namibia and Botswana [m]) - 1,600 km
note: [s] after country name indicates river source; [m] after country name indicates river mouth
Major watersheds (area sq km)
Atlantic Ocean drainage: Congo (3,730,881 sq km)
Indian Ocean drainage: Zambezi (1,332,412 sq km)
Internal (endorheic basin) drainage: Okavango Basin (863,866 sq km)
Major aquifers
Congo Basin, Upper Kalahari-Cuvelai-Upper Zambezi Basin
Population distribution
most people live in the western half of the country; urban areas account for the highest concentrations of people, particularly the capital of Luanda
Natural hazards
locally heavy rainfall causes periodic flooding on the plateau
Geography - note
the province of Cabinda is an exclave, separated from the rest of the country by the Democratic Republic of the Congo
People and Society
Population
total: 37,202,061 (2024 est.)
male: 18,196,058
female: 19,006,003
comparison rankings: total 40; male 42; female 39
Nationality
noun: Angolan(s)
adjective: Angolan
Ethnic groups
Ovimbundu 37%, Kimbundu 25%, Bakongo 13%, Mestico (mixed European and native African) 2%, European 1%, other 22%
Languages
Portuguese 71.2% (official), Umbundu 23%, Kikongo 8.2%, Kimbundu 7.8%, Chokwe 6.5%, Nhaneca 3.4%, Nganguela 3.1%, Fiote 2.4%, Kwanhama 2.3%, Muhumbi 2.1%, Luvale 1%, other 3.6% (2014 est.)
note: shares sum to more than 100% because some respondents gave more than one answer on the census
Religions
Roman Catholic 41.1%, Protestant 38.1%, other 8.6%, none 12.3% (2014 est.)
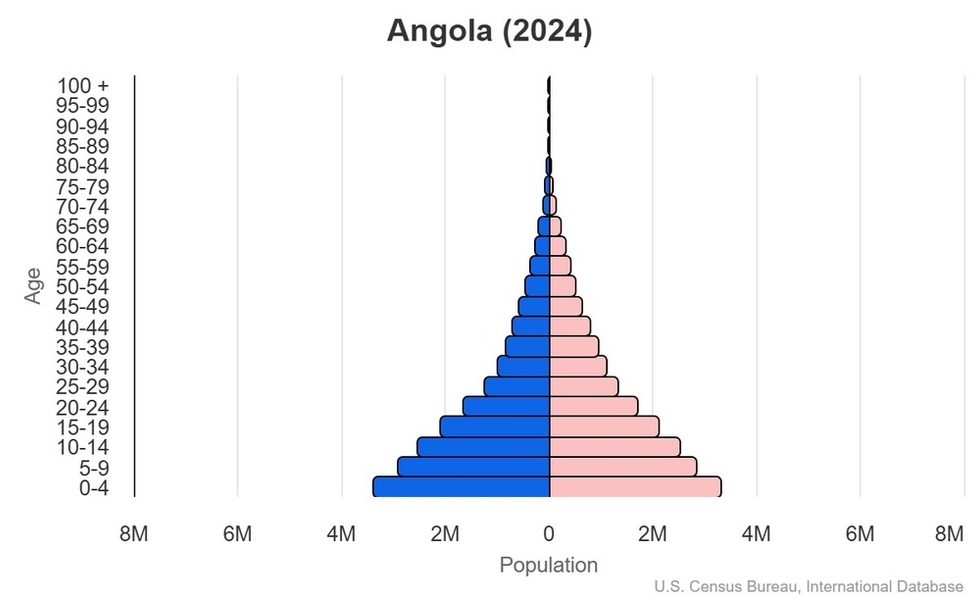
Age structure
0-14 years: 46.9% (male 8,752,419/female 8,701,422)
15-64 years: 50.7% (male 9,076,080/female 9,795,035)
65 years and over: 2.4% (2024 est.) (male 367,559/female 509,546)
Dependency ratios
total dependency ratio: 96.1 (2024 est.)
youth dependency ratio: 91.1 (2024 est.)
elderly dependency ratio: 5.1 (2024 est.)
potential support ratio: 19.8 (2024 est.)
Median age
total: 16.3 years (2024 est.)
male: 15.8 years
female: 16.8 years
comparison ranking: total 227
Population distribution
most people live in the western half of the country; urban areas account for the highest concentrations of people, particularly the capital of Luanda
Urbanization
urban population: 68.7% of total population (2023)
rate of urbanization: 4.04% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Major urban areas - population
9.292 million LUANDA (capital), 959,000 Lubango, 905,000 Cabinda, 809,000 Benguela, 783,000 Malanje (2023)
Sex ratio
at birth: 1.03 male(s)/female
0-14 years: 1.01 male(s)/female
15-64 years: 0.93 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.72 male(s)/female
total population: 0.96 male(s)/female (2024 est.)
Mother's mean age at first birth
19.4 years (2015/16 est.)
note: data represents median age at first birth among women 20-49
Infant mortality rate
total: 55.6 deaths/1,000 live births (2024 est.)
male: 60.7 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 50.3 deaths/1,000 live births
comparison ranking: total 13
Life expectancy at birth
total population: 62.9 years (2024 est.)
male: 60.8 years
female: 65.1 years
comparison ranking: total population 214
Gross reproduction rate
2.81 (2024 est.)
Drinking water source
improved:
urban: 71.7% of population (2022 est.)
rural: 27.8% of population (2022 est.)
total: 57.7% of population (2022 est.)
unimproved:
urban: 28.3% of population (2022 est.)
rural: 72.2% of population (2022 est.)
total: 42.3% of population (2022 est.)
Health expenditure
3% of GDP (2021)
6.7% of national budget (2022 est.)
Physician density
0.24 physicians/1,000 population (2022)
Hospital bed density
0.8 beds/1,000 population (2019 est.)
Sanitation facility access
improved:
urban: 93.7% of population (2022 est.)
rural: 30.3% of population (2022 est.)
total: 73.5% of population (2022 est.)
unimproved:
urban: 6.3% of population (2022 est.)
rural: 69.7% of population (2022 est.)
total: 26.5% of population (2022 est.)
Alcohol consumption per capita
total: 5.84 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
beer: 3.78 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
wine: 0.72 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
spirits: 1.27 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
other alcohols: 0.08 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
comparison ranking: total 73
Currently married women (ages 15-49)
55.7% (2023 est.)
Child marriage
women married by age 15: 7.9% (2016)
women married by age 18: 30.3% (2016)
men married by age 18: 6% (2016)
Education expenditure
2.5% of GDP (2023 est.)
6.5% national budget (2025 est.)
comparison ranking: Education expenditure (% GDP) 173
Literacy
total population: 66.2% (2015 est.)
male: 83.8% (2015 est.)
female: 51.9% (2015 est.)
Environment
Environmental issues
overuse of pastures and subsequent soil erosion; desertification; deforestation of tropical rainforest from international demand for timber and domestic use as fuel; loss of biodiversity; soil erosion contributing to water pollution and siltation of rivers and dams; inadequate supplies of potable water
International environmental agreements
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Climate Change-Paris Agreement, Comprehensive Nuclear Test Ban, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping-London Protocol, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution
signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements
Climate
semiarid in south and along coast to Luanda; north has cool, dry season (May to October) and hot, rainy season (November to April)
Land use
agricultural land: 36.8% (2022 est.)
arable land: 4.3% (2022 est.)
permanent crops: 0.3% (2022 est.)
permanent pasture: 32.3% (2022 est.)
forest: 52.5% (2022 est.)
other: 10.6% (2022 est.)
Urbanization
urban population: 68.7% of total population (2023)
rate of urbanization: 4.04% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Carbon dioxide emissions
19.66 million metric tonnes of CO2 (2023 est.)
from coal and metallurgical coke: 9,000 metric tonnes of CO2 (2023 est.)
from petroleum and other liquids: 17.21 million metric tonnes of CO2 (2023 est.)
from consumed natural gas: 2.441 million metric tonnes of CO2 (2023 est.)
comparison ranking: total emissions 86
Particulate matter emissions
27.2 micrograms per cubic meter (2019 est.)
Methane emissions
energy: 1,009.1 kt (2022-2024 est.)
agriculture: 374.5 kt (2019-2021 est.)
waste: 123 kt (2019-2021 est.)
other: 78.5 kt (2019-2021 est.)
Waste and recycling
municipal solid waste generated annually: 4.214 million tons (2024 est.)
percent of municipal solid waste recycled: 19% (2022 est.)
Total water withdrawal
municipal: 319.5 million cubic meters (2022 est.)
industrial: 239.6 million cubic meters (2022 est.)
agricultural: 146.7 million cubic meters (2022 est.)
Total renewable water resources
148.4 billion cubic meters (2022 est.)
Government
Country name
conventional long form: Republic of Angola
conventional short form: Angola
local long form: Republica de Angola
local short form: Angola
former: People's Republic of Angola
etymology: in the 15th century, Portuguese explorers derived the name from the title "N'gola," which was held by kings of the Ndongo
Government type
presidential republic
Capital
name: Luanda
geographic coordinates: 8 50 S, 13 13 E
time difference: UTC+1 (6 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
daylight saving time: does not observe daylight savings time
etymology: the Portuguese named the city São Paulo da Assunção de Loanda (Saint Paul of the Assumption of Loanda); over time, it was shortened to "Luanda," which may derive from a Bantu word meaning "tax" or "duty," in reference to local people paying their dues to the king of the Congo
Administrative divisions
21 provinces (provincias, singular - provincia); Bengo, Benguela, Bie, Cabinda, Cuando, Cubango, Cuanza-Norte, Cuanza-Sul, Cunene, Huambo, Huila, Icolo e Bengo, Luanda, Lunda-Norte, Lunda-Sul, Malanje, Moxico, Moxico Leste, Namibe, Uige, Zaire
Legal system
civil legal system based on Portuguese civil law; no judicial review of legislation
Constitution
history: previous 1975, 1992; latest passed by National Assembly 21 January 2010, adopted 5 February 2010
amendment process: proposed by the president of the republic or supported by at least one third of the National Assembly membership; passage requires at least two-thirds majority vote of the Assembly subject to prior Constitutional Court review if requested by the president of the republic
International law organization participation
has not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; non-party state to the ICCt
Citizenship
citizenship by birth: no
citizenship by descent only: at least one parent must be a citizen of Angola
dual citizenship recognized: no
residency requirement for naturalization: 10 years
Suffrage
18 years of age; universal
Executive branch
chief of state: President Joao Manuel Goncalves LOURENCO (since 26 September 2017)
head of government: President Joao Manuel Goncalves LOURENCO (since 26 September 2017)
cabinet: Council of Ministers appointed by the president
election/appointment process: the candidate of the winning party or coalition in the last legislative election becomes the president; president serves a 5-year term (eligible for a second consecutive or discontinuous term)
most recent election date: 24 August 2022
election results: Joao Manuel Goncalves LOURENCO (MPLA) elected president by then winning party following the 24 August 2022 general election
expected date of next election: 2027
Legislative branch
legislature name: National Assembly (Assembleia nacional)
legislative structure: unicameral
number of seats: 220 (all directly elected)
electoral system: proportional representation
scope of elections: full renewal
term in office: 5 years
most recent election date: 8/24/2022
parties elected and seats per party: Popular Movement for the Liberation of Angola (MPLA) (124); National Union for the Total Independence of Angola (UNITA) (90); Other (6)
percentage of women in chamber: 39.1%
expected date of next election: August 2027
Judicial branch
highest court(s): Supreme Court or Tribunal Supremo (consists of the court president, vice president, and a minimum of 16 judges); Constitutional Court or Tribunal Constitucional (consists of 11 judges)
judge selection and term of office: Supreme Court judges appointed by the president on recommendation of the Supreme Judicial Council, an 18-member body chaired by the president; judge tenure NA; Constitutional Court judges - 4 nominated by the president, 4 elected by National Assembly, 2 elected by Supreme National Council, 1 elected by competitive submission of curricula; judges serve single 7-year terms
subordinate courts: provincial and municipal courts
Political parties
Broad Convergence for the Salvation of Angola Electoral Coalition or CASA-CE
Humanist Party of Angola or PHI
National Front for the Liberation of Angola or FNLA; note - party has two factions
National Union for the Total Independence of Angola or UNITA (largest opposition party)
Popular Movement for the Liberation of Angola or MPLA; note- ruling party in power since 1975
Social Renewal Party or PRS
Diplomatic representation in the US
chief of mission: Ambassador Agostinho de Carvalho dos Santos VAN-DÚNEM (since 30 June 2023)
chancery: 2108 16th Street NW, Washington, DC 20009
telephone: [1] (202) 785-1156
FAX: [1] (202) 822-9049
email address and website:
info@angola.org
https://angola.org/
consulate(s) general: Houston, New York
Diplomatic representation from the US
chief of mission: Ambassador (vacant); Chargé d’Affaires Ambassador Noah ZARING (since March 2025)
embassy: Rua Houari Boumedienne, #32, Luanda
mailing address: 2550 Luanda Place, Washington, DC 20521-2550
telephone: [244] (222) 64-1000
FAX: [244] (222) 64-1000
email address and website:
Consularluanda@state.gov
https://ao.usembassy.gov/
International organization participation
ACP, AfDB, AU, CEMAC, CPLP, FAO, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO (correspondent), ITSO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), MIGA, NAM, OAS (observer), SADC, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNMISS, Union Latina, UNOOSA, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO
Independence
11 November 1975 (from Portugal)
National holiday
Independence Day, 11 November (1975)
Flag
description: two equal horizontal bands of red (top) and black with a centered yellow emblem of a five-pointed star inside half a cogwheel, crossed by a machete (in the style of a hammer and sickle)
meaning: red stands for liberty and black for the African continent; the emblem symbolizes workers and peasants
National symbol(s)
giant black sable antelope (Palanca negra gigante)
National color(s)
red, black, yellow
National anthem(s)
title: "Angola Avante" (Forward Angola)
lyrics/music: Manuel Rui Alves MONTEIRO/Rui Alberto Vieira Dias MINGAO
history: adopted 1975
National heritage
total World Heritage Sites: 1 (cultural)
selected World Heritage Site locales: Mbanza-Kongo
Economy
Economic overview
middle-income, oil-dependent African economy; widespread poverty; rising inflation and currency depreciation; seeking diversification through agricultural production; significant corruption in public institutions; major infrastructure investments from China and US; exited OPEC in 2023
Real GDP (purchasing power parity)
$278.239 billion (2024 est.)
$266.452 billion (2023 est.)
$263.61 billion (2022 est.)
note: data in 2021 dollars
comparison ranking: 64
Real GDP growth rate
4.4% (2024 est.)
1.1% (2023 est.)
3% (2022 est.)
note: annual GDP % growth based on constant local currency
comparison ranking: 55
Real GDP per capita
$7,300 (2024 est.)
$7,300 (2023 est.)
$7,400 (2022 est.)
note: data in 2021 dollars
comparison ranking: 154
GDP (official exchange rate)
$80.397 billion (2024 est.)
note: data in current dollars at official exchange rate
Inflation rate (consumer prices)
28.2% (2024 est.)
13.6% (2023 est.)
21.4% (2022 est.)
note: annual % change based on consumer prices
comparison ranking: 195
GDP - composition, by sector of origin
agriculture: 16.4% (2024 est.)
industry: 44.2% (2024 est.)
services: 39.3% (2024 est.)
note: figures may not total 100% due to non-allocated consumption not captured in sector-reported data
comparison rankings: agriculture 51; industry 14; services 194
GDP - composition, by end use
household consumption: 55.3% (2024 est.)
government consumption: 6.3% (2024 est.)
investment in fixed capital: 25% (2024 est.)
investment in inventories: 0% (2024 est.)
exports of goods and services: 37.9% (2024 est.)
imports of goods and services: -24.4% (2024 est.)
note: figures may not total 100% due to rounding or gaps in data collection
Agricultural products
cassava, bananas, maize, sweet potatoes, sugarcane, tomatoes, pineapples, onions, potatoes, citrus fruits (2023)
note: top ten agricultural products based on tonnage
Industries
petroleum; diamonds, iron ore, phosphates, feldspar, bauxite, uranium, and gold; cement; basic metal products; fish processing; food processing, brewing, tobacco products, sugar; textiles; ship repair
Industrial production growth rate
5% (2024 est.)
note: annual % change in industrial value added based on constant local currency
comparison ranking: 44
Labor force
15.961 million (2024 est.)
note: number of people ages 15 or older who are employed or seeking work
comparison ranking: 41
Unemployment rate
14.5% (2024 est.)
14.6% (2023 est.)
14.7% (2022 est.)
note: % of labor force seeking employment
comparison ranking: 172
Youth unemployment rate (ages 15-24)
total: 27.9% (2024 est.)
male: 30.2% (2024 est.)
female: 25.7% (2024 est.)
note: % of labor force ages 15-24 seeking employment
comparison ranking: total 26
Population below poverty line
32.3% (2018 est.)
note: % of population with income below national poverty line
Gini Index coefficient - distribution of family income
51.3 (2018 est.)
note: index (0-100) of income distribution; higher values represent greater inequality
comparison ranking: 7
Average household expenditures
on food: 50% of household expenditures (2023 est.)
on alcohol and tobacco: 1.4% of household expenditures (2023 est.)
Household income or consumption by percentage share
lowest 10%: 1.3% (2018 est.)
highest 10%: 39.6% (2018 est.)
note: % share of income accruing to lowest and highest 10% of population
Remittances
0% of GDP (2024 est.)
0% of GDP (2023 est.)
0% of GDP (2022 est.)
note: personal transfers and compensation between resident and non-resident individuals/households/entities
Budget
revenues: $18.117 billion (2019 est.)
expenditures: $13.871 billion (2019 est.)
note: central government revenues and expenses (excluding grants/extrabudgetary units/social security funds) converted to US dollars at average official exchange rate for year indicated
Taxes and other revenues
10.1% (of GDP) (2019 est.)
note: central government tax revenue as a % of GDP
comparison ranking: 127
Current account balance
$6.31 billion (2024 est.)
$4.185 billion (2023 est.)
$11.763 billion (2022 est.)
note: balance of payments - net trade and primary/secondary income in current dollars
comparison ranking: 33
Exports
$36.924 billion (2024 est.)
$36.961 billion (2023 est.)
$50.12 billion (2022 est.)
note: balance of payments - exports of goods and services in current dollars
comparison ranking: 77
Exports - partners
China 40%, India 9%, UAE 6%, Spain 6%, Netherlands 5% (2023)
note: top five export partners based on percentage share of exports
Exports - commodities
crude petroleum, diamonds, natural gas, ships, refined petroleum (2023)
note: top five export commodities based on value in dollars
Imports
$22.683 billion (2024 est.)
$23.688 billion (2023 est.)
$28.564 billion (2022 est.)
note: balance of payments - imports of goods and services in current dollars
comparison ranking: 92
Imports - partners
China 19%, Portugal 10%, UAE 7%, India 6%, USA 5% (2023)
note: top five import partners based on percentage share of imports
Imports - commodities
refined petroleum, wheat, ships, cars, trucks (2023)
note: top five import commodities based on value in dollars
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold
$14.243 billion (2024 est.)
$13.942 billion (2023 est.)
$13.655 billion (2022 est.)
note: holdings of gold (year-end prices)/foreign exchange/special drawing rights in current dollars
comparison ranking: 70
Debt - external
$45.299 billion (2023 est.)
note: present value of external debt in current US dollars
comparison ranking: 16
Exchange rates
kwanza (AOA) per US dollar -
Exchange rates:
869.846 (2024 est.)
685.02 (2023 est.)
460.568 (2022 est.)
631.442 (2021 est.)
578.259 (2020 est.)
Energy
Electricity access
electrification - total population: 48.5% (2022 est.)
electrification - urban areas: 76.2%
electrification - rural areas: 7.3% (2018 est.)
Electricity
installed generating capacity: 7.6 million kW (2023 est.)
consumption: 16.214 billion kWh (2023 est.)
transmission/distribution losses: 1.725 billion kWh (2023 est.)
comparison rankings: installed generating capacity 74; consumption 83; transmission/distribution losses 118
Electricity generation sources
fossil fuels: 23.6% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
solar: 2.2% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
hydroelectricity: 74% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
biomass and waste: 0.3% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
Coal
imports: 3,000 metric tons (2023 est.)
Petroleum
total petroleum production: 1.175 million bbl/day (2023 est.)
refined petroleum consumption: 121,000 bbl/day (2023 est.)
crude oil estimated reserves: 7.783 billion barrels (2021 est.)
Natural gas
production: 5.984 billion cubic meters (2023 est.)
consumption: 1.244 billion cubic meters (2023 est.)
exports: 4.928 billion cubic meters (2023 est.)
proven reserves: 343.002 billion cubic meters (2021 est.)
Communications
Telephones - fixed lines
total subscriptions: 87,000 (2023 est.)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: (2023 est.) less than 1
comparison ranking: total subscriptions 138
Telephones - mobile cellular
total subscriptions: 25.7 million (2023 est.)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 67 (2022 est.)
comparison ranking: total subscriptions 54
Broadcast media
state-owned media dominate; only four privately owned newspapers still exist in print form; state-run Radio Nacional de Angola (RNA) is the only outlet to offer programs in local languages such as Bantu; private stations operate in cities, including Catholic Radio Ecclesia, but RNA is the only radio broadcaster with near-national coverage (2023)
Internet users
percent of population: 45% (2023 est.)
Broadband - fixed subscriptions
total: 137,000 (2023 est.)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: (2023 est.) less than 1
comparison ranking: total 126
Transportation
Railways
total: 2,761 km (2022)
narrow gauge: 2,638 km (2022) 1.067-m gauge
123 km 0.600-mm gauge
Merchant marine
total: 64 (2023)
by type: general cargo 13, oil tanker 8, other 43
comparison ranking: total 112
Ports
total ports: 21 (2024)
large: 0
medium: 0
small: 8
very small: 13
ports with oil terminals: 17
key ports: Cabinda, Estrela Oil Field, Lobito, Luanda, Malongo Oil Terminal, Namibe, Palanca Terminal, Takula Terminal
Military and Security
Military and security forces
Angolan Armed Forces (Forcas Armadas Angolanas, FAA): Army, Navy (Marinha de Guerra Angola, MGA), Angolan National Air Force (Forca Aerea Nacional Angolana, FANA)
Ministry of Interior: National Police, Border Guard Police (2025)
Military expenditures
1% of GDP (2024 est.)
1.3% of GDP (2023 est.)
1.3% of GDP (2022 est.)
1.4% of GDP (2021 est.)
1.7% of GDP (2020 est.)
Military and security service personnel strengths
approximately 100,000 active-duty Armed Forces (2025)
Military equipment inventories and acquisitions
most Angolan military weapons and equipment are of Russian or Soviet-era origin; there are smaller quantities of items originating from such suppliers as China, Brazil, and South Africa (2024)
Military service age and obligation
20-45 years of age for compulsory and 18-45 years for voluntary military service for men (registration at age 18 is mandatory); 20-45 years of age for voluntary service for women; 24-month conscript service obligation; Angolan citizenship required; the Navy is entirely staffed with volunteers (2023)
Military - note
the Angolan Armed Forces were created in 1991 under the Bicesse Accords signed between the Angolan Government and the National Union for the Total Independence of Angola (UNITA); the current force is responsible for country’s external defense but also has some domestic security responsibilities, such as border protection; it participates in multinational exercises, as well as regional peacekeeping operations, including the deployment of several hundred troops to the Democratic Republic of the Congo in 2023; in recent years, the military has placed additional emphasis on maritime security and protecting offshore resources (2025)
Space
Space agency/agencies
National Space Program Office (Gabinete de Gestão do Programa Espacial Nacional, GGPEN; established 2013) (2025)
Space program overview
has a national space strategy with a focus on capacity-building, developing space infrastructure, investing in domestic space sector, supporting socioeconomic growth, and establishing cooperation agreements with foreign technical and scientific institutions in the space industry; contracts with foreign companies to build and launch satellites; operates satellites; cooperates with a variety of foreign space agencies and industries, including those of France, Portugal, Russia, the US, and other African countries; member of the African Space Agency (2025)
note: further details about the key activities, programs, and milestones of the country’s space program, as well as government spending estimates on the space sector, appear in the Space Programs reference guide
Transnational Issues
Refugees and internally displaced persons
refugees: 55,542 (2024 est.)
IDPs: 75,308 (2024 est.)



